hypertension
15-20 million people in Germany suffer from high blood pressure (hypertension). Only 10% of the cases of high blood pressure can be attributed to a specific cause. This is called secondary hypertension. Causes may be as kidney disease or a narrowing of the main artery (aorta). In 90% of all cases can not (yet) do not trigger the underlying disease (primary hypertension). There are only risk factors that make the occurrence of primary hypertension likely. These include physical inactivity, obesity, Smoking, frequent and heavy alcohol consumption, diabetes (diabetes), but also about long working hours (see also research date of 21 October 2006: "Long hours harm to health") and stress. In some cases, lifestyle changes alone can normalize blood pressure, failing a drug therapy is essential because untreated, chronically elevated blood pressure has serious consequences. These include heart failure (heart failure), stroke, brain hemorrhage and blood vessel damage that can lead to circulation problems, heart attacks and kidney damage.
Blood pressure is generated by the pumping of the heart in the blood vessel system of arteries (high-pressure system) and veins (low pressure system). It depends on the with every heartbeat in the main artery (aorta) depressed blood flow (stroke volume) and the flow resistance of the blood vessel system, ie the length and elasticity of blood vessels, especially the high-pressure system.

main artery (aorta)
(from Wikipedia)
more rigid and narrow the vessels are, the more pressure can build up under the same Hezschlagvolumen. The blood pressure varies and is the contraction the heart muscle, so the actual pumping (systole) than for the relaxation of the heart (diastole). This creates a palpable pulse and the two blood pressure values. The first number is the systolic, the second number is the diastolic blood pressure. Optimal values are mm Hg, 120/80, 130/80-90 still normal, values of as high normal values of 135-140/85-90 are and everything about it is already more or less pathological.
Normal blood pressure is the result of ongoing focal-control processes. By pressure-sensitive nerve endings (pressure sensors) in the wall of the aorta and the carotid arteries, the circulation center in the brain (brain stem) immediately informed if the blood pressure rises or falls and controls it. It is a short, medium and long-term effective control.
responds the short term, the autonomic nervous system. In a blood pressure drop, the activity of the sympathetic neurotransmitter norepinephrine with his and the activity of the parasympathetic neurotransmitter acetylcholine from his. An increase in cardiac activity and the (peripheral, ie marginal) blood vessels constrict, so that the blood pressure rises again. With a rise in blood pressure, it behaves just the opposite.
Keywords: autonomic nervous system The autonomic nervous system controls together with the endocrine (Endocrine = inward directly into the blood) system (hormones) the inner world's (human) organism. It is true the functions of internal organs quickly to the needs of the organism from, because the neural control allows for very rapid adaptation, while the endocrine system, the functional state of the internal organs regulates long-term. The autonomic nervous system, the central portions of the brain stem, hypothalamus and spinal cord are located, is divided into a sympathetic component (sympathetic) and into a parasympathetic component (parasympathetic), the opponents are. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system (neurotransmitter noradrenaline) puts the organism into a state of increased readiness to perform: Cardiac force, heart rate and blood pressure increase, the muscle blood flow increases, the bronchi dilate (better breathing), is for better energy released in the liver glucose from the glycogen and fat stores are broken down more restricted all digestive processes and the pupils weitgestellt.Der parasympathetic is however, during periods of rest (recovery period) of the organism activated: reducing heart force and heart rate, blood pressure and narrowing of the bronchi, salivation, and increased activity of the digestive tract, and pupil constriction.
out medium term, a blood pressure-triggered by reduced blood flow to increased renin-education and distribution in the kidney. Renin is an enzyme that converts angiotensinogen occurring in the blood - a small protein formed in the liver - by cleavage to angiotensin I by. Another occurring in the walls of blood vessels enzyme ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II by. Angiotensin II acts very much on the smooth muscle of blood vessels that constrict the fact so that the blood pressure rises again. Angiotensin also destroyed in the blood also occurring kinins, small proteins that extend as signal substances normally the blood vessels (bradykinin, Substance P). Also will help raise your blood pressure again. In a blood pressure rise is all the other way around.
Keywords: Enzyme enzymes are complex molecules built protein (proteins) that are used in all cells but also extracellularly (outside the cell) before and act as biocatalysts. They accelerate like all catalysts, chemical reactions, without having to change themselves and act in this very specific, that they accept only certain chemical compounds, their substrates, and they provide only very specific chemical reactions. They thus in the first place a regular metabolism by selecting certain reactions possible in principle. Enzymes control the metabolism, as they change their activity under the influence of signal substances and thus adapt the metabolism of the respective situation.
has long term angiotensin II also addresses the adrenal cortex, which then secretes the hormone aldosterone increases. Aldosterone ensures that the kidney excretes less sodium ions, but which can be retained only with their water solution. The amount of fluid in the blood vessels increases. The retained sodium ions accumulate in the blood vessel walls, making them much more sensitive to the neurotransmitter noradrenaline, the sympathetic . Both processes can lead to high blood pressure. The well-known fact that too much favor common salt (sodium chloride), high blood pressure can thus also be well explained. A blood pressure increase in turn triggers exactly the opposite processes. The
just discussed in blood pressure control processes provide targets for drug therapy:
Sympathikushemmer act directly on the circulatory system in the brain, where they reduce the activity of the autonomic nervous system Sympathikusanteils and therefore reduce blood pressure. They are preferred in severe hypertension. Common side effects include slow heart beat (bradycardia), sedation (sedation), dry mouth and impotence.
are examples: clonidine (Catapresan (R)) , Metyldopa (Presinol (R)) that interfere in addition, the norepinephrine synthesis (see below) and dihydralazine (Nepresol (R) ) .
Entspeicherer / false precursor lead to a deficiency of norepinephrine in the nerve endings (synapses) of the sympathetic nervous system and thus inhibit its effect the blood vessels, causing them further and drops in blood pressure. guanethidine (Esimil (R)) and reserpine (Briserin (R)) raise storage capacity of the bubbles (vesicles) in which norepinephrine is stored prior to distribution, while methyldopa (Presinol ( R) , above) interfere as false precursor, the synthesis of noradrenaline in the nerve endings by a false neurotransmitter is formed.
Keywords: Nerve cells nerve cells (neurons) are electrical Specialized conduction cells are the building blocks of the nervous system. They consist of a cell body (soma), tree-like branched processes of the cell body, the dendrites, which receive from other nerve cells, emotions, and a further single, long extension, the axon that conveys the excitement of contact points (synapses) to other nerve cells. A nerve cell can have up to 10,000 synapses. While the excitement within a nerve cell propagates purely electric, the excitation is transmitted from one to the other nerve cell by signaling molecules that are stored by the synapses of a nerve cell in vesicles and released during an incoming electrical excitation be. These so-called neurotransmitter release at the dendrites of the receiving nerve cell - after binding to specific receptors - again, an electrical excitation from. Afterwards, the neurotransmitter enzymatically degraded and the receptors are free again. Nerve cells can not only attract other nerve cells, but also other target cells through release of neurotransmitters such as muscle cells or glands.
The electrical excitation of nerve cells (or other cells) is done as follows: The nerve cell is like all other cells from a semi-fluid lipid bilayer membrane surrounded. Lipids are fatty substances with a long fat-soluble and a short water-soluble fraction. The fat-soluble components are in the bilayer membrane facing each other, the water-soluble components have one outside and one inside. In the membrane mosaic proteins are embedded. When the proteins are enzymes (see above), receptors (see below) or if they extend from the outside in, forming a kind of tube is it's ion channels. In the water surrounding the cell membrane are positively charged Natium, potassium and calcium ions and negatively charged chloride ions and ion water.The protein has enzymatic cell membrane ion pumps that use energy to sodium ions outward and potassium ions move inward. The diaphragm is apart from the ion channels for ion virtually impermeable. In the rest of the nerve cell, only the potassium channels are open. Since the ion pump is inside a potassium ion excess they migrate along the concentration gradient through the potassium channels open to the outside. Since not come behind the negatively charged ions produced inside and outside a positive, a negative charge excess between which an electric field is created. This is getting bigger, until finally, it prevents further migration of positively charged potassium ions to the outside. It is a so-called resting potential, because without the migration of potassium ions, the electric field not be stronger. Now bind the neurotransmitters to their receptors on the nerve cell, or decrease the resting potential by another electric field, as in the conduction within the nerve cell, then open up suddenly, the sodium channels (and also slower calcium channels), the positively charged sodium ions (calcium ions ) flow along their concentration gradient from outside to inside and the potassium channels close. The resting potential collapses, and there is an action potential with the opposite Ladungsverhältnissen.Nach short time, the potassium channels open again, and the ion pump in place by now closed sodium channels, the resting potential Restore.
alpha blockers cause an enlargement of the peripheral (marginal) blood vessels by blocking alpha receptors located there for norepinephrine, the neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system loses its influence on the (smooth) muscle of the peripheral blood vessels. The muscles are relaxed, the blood vessels and further decreases in blood pressure. However, the sympathetic effect, the cardiovascular center in the brain stem and the renin-angiotensin mechanism (see above) of the blood pressure lowering and lifting against the first drop in blood pressure was at least partly on again. Remedy is by addition of beta-blockers (calming the heart, inhibition of renin release) and diuretics possible (see below). Known alpha blockers doxazosin are (Cardular (R)) , prazosin (Minipress (R)) and urapidil (Ebrantil (R)) , which in addition also a direct Sympathikushemmer (so) .
Keywords: receptors receptors are receiving mechanisms that respond to each specific body's own signaling molecules (hormones, neurotransmitters) or exogenous substances (drugs) specifically. The receptors are proteins and are often found in cell membranes, but often also in the cytoplasm or the nucleus. Each receptor protein molecule has a binding site, a kind of bag that is shaped to a different, usually much smaller molecule, the signal or agent, here as a key fits into a lock. This key is then a suitable agonist, causing a deformation of the receptor molecule, which is then triggered a signal or an effect. Substances that are similar to the agonist, but can not exactly fit the bag to block the receptor molecule, without causing deformation. These so-called Antagonists (antagonist) compete with the agonist to the same receptor binding site and, thus, prevent the triggering of a signal or an effect.
Beta blockers block the beta- receptors for norepinephrine, the neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system, its effect decreases it. A distinction is beta-1 receptors, which occur mainly in the heart (increased heart force and heart rate) and kidney (increased renin formation) and beta-2 receptors in the lungs (bronchodilator), liver (increased breakdown of glycogen to glucose, an energy carrier), as in fat cells (mobilization of fat reserves of energy) and in the small arterial blood vessels (expansion, improved blood flow as the muscle) are found. A blockade of the beta-1 receptors slows the heart, reduces the amount of formed in the kidney renin (attenuation of the renin-Angitensin mechanism), thereby reducing blood pressure. The beta 2-blockade, however, difficult breathing, as the bronchial tubes are close by (caution in patients with spastic bronchitis or asthma!). Angestebt is therefore a possible selective beta-1 blockade. This was achieved quite well in atenolol (Tenormin (R)) , bisoprolol (Concor (R)) and metoprolol (Beloc (R)) . Non-selective beta blockers propranolol are (Dociton (R)) , sotalol (Sotalex (R)) and Carvedilol (carvedilol (R)), blocks which not only beta-receptors but also the alpha- receptors in the peripheral blood vessels, so that these extended. celiprolol (Selectol (R)) blocks beta-1 and activates the blutgefäßerweiternden beta-2 receptors.
Common side effects of beta blockers are headache, dizziness and fatigue as a sign of excessive blood pressure reduction. Continue to emerge gastrointestinal probems and erectile dysfunction.
ACE - inhibitors block the enzyme ACE and thus the formation of strong vasoconstrictive angiotensin II (see above). The reduced formation of angiotensin II also leads to reduced aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex, resulting in less fluid is retained by the kidney. The amount of fluid in the blood vessels decreases. The increased excretion of dissolved salt can decrease the sodium ion concentration in the blood vessel walls, thereby decreasing their responsiveness to the sympathetic vasoconstriction acting (see above). All this lowers denBlutdruck. Since the ACE enzyme normally blutgefäßerweiternde kinins (above) breaks down, it comes through the ACE-blockade in an increased incidence of these small proteins (bradykinin, substance P) in the blood. This supports the one hand, the target blood pressure-lowering effect, on the other hand, these substances irritate the bronchial tubes, which can lead to severe coughing. Of these most common side effect of ACE inhibitors affect up to 30% of patients.
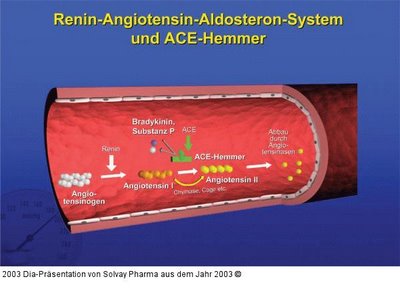
ACE inhibitors should not be combined with potassium-sparing diuretics (see below), otherwise an excessive accumulation of potassium ions in the blood comes. It is then the risk of life-threatening Heart rhythm disturbances in cardiac arrest! are in contrast to the beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors metabolically neutral, meaning they have no influence on lipid and glucose metabolism and protect the kidneys. Both are especially important in diabetics. The most ACE inhibitors are captopril (Lopirin (R)) , enalapril (Xanef (R)) , lisinopril (Zestril (R)) and ramipril (Delix (R)) .
AT-II blocker (Angiotensinantagonisten) displace angiotensin II from its receptor binding site and keep then all effects of Angiotensin II (above) more or less. The blood pressure drops. Since there is no ACE inhibition, not even the kinins appear increasingly in the blood, so that the typical ACE inhibitor cough absent (see above). The AT-II blockers may be in no case with potassium-sparing diuretics (see below) taken together. Known AT-II blocker candesartan are (Blopress (R)) , losartan (Lorzaar (R)) and valsartan (Diovan (R) , Provas (R)) .
calcium antagonists directly expand the blood vessels, thereby including vascular smooth muscles relax, so that the blood pressure decreases. They do this by blocking the slow Calciumioneneinstrom in the muscle cells. The smooth muscles to contract is no longer with excitement. At the same time aggravate calcium antagonists, the electrical stimulation of the muscles, which allows calcium influx and thus the contraction of muscles. A distinction is selective calcium antagonists such as nifedipine (Adalat (R)) , nitrendipine (Bayotensin (R)) and amlodipine (Norvasc (R)) of non-selective calcium antagonist, not only on vascular muscle but also effect on heart muscles, such as verapamil (Isoptin (R)) and diltiazem (Dilz (R)) . Non-selective calcium channel blockers may not be used in heart failure (heart failure).
calcium antagonists often cause a sudden, but transient skin redness (flushing) and headache due to the widening of the (arterial) blood vessels.
Keywords: muscle The muscles consist of elongated fibers that zsammenziehen at the arrival of an electrical stimulus (muscle contraction). The muscle fibers are made of parallel threads umeinanderliegenden protein involved in the contraction (shortening or tension slide into each other) telescope. This process is triggered by calcium ions flow during electrical stimulation in the muscle cells and then attach themselves to the protein filaments. After contraction, the calcium ions leave the protein filaments again, which then languish until the next contraction. The muscular contraction of course, require energy that is provided in the form of the energy-rich substance ATP (adenosine triphosphate). In the cleavage of ATP, the energy is then released. The ATP in turn is formed in the "cold combustion" of nutrients such as glucose or fats.
There are skeletal muscles that the voluntary control and are subject to contract quickly contract smooth muscles, which are controlled by the autonomic nervous system and slow. Then there are the heart muscle that are similar to the skeletal muscles, but not (usually) subject to the will, but are also controlled vegetative.
nitrates cause an enzymatically mediated release of the signal substance NO (nitric oxide) in the blood vessel wall. The NO enters the vascular smooth muscle and activated there an enzymatic reaction chain that leads to a decrease in calcium ion concentration, after which the muscles relax. The arterial vessels are more and blood pressure decreases. Also, the veins will continue to hold more blood. The heart is relieved by the same course through the lower blood pressure. Known nitrates the nitroglycerin (Nitrolingual (R)) are is, however, degrade rapidly in the liver and therefore be administered as a spray or Zerbeißkapsel must the isosorbide dinitrate (Isoket (R)) that isosorbide mononitrate (CONPIN (R)) and molsidomine (CORVATON (R)) . Nitrates are primarily in the presence of angina pectoris (chest tightness) was used in which a discrepancy between oxygen demand of the heart muscle and the oxygen supply. It is then particularly to a discharge to the heart to correct this imbalance.
more direct vessel effective blood pressure medicines are Minoxidil (Lonolox (R)) , it opens the potassium channels, after which the potassium ions leave the muscle and the vessels limp ; dihydralazine (Nepresol (R)) , it inhibits mediated by the signal substance IP3 (inositol triphosphate), the release of the slow Calcium ions (see above) from their location, the ER (endoplasmic reticulum), a membrane-tube network within the muscle cells, so that losing the vessel walls their tension and cicletanine (Justar (R)) , it increases the blood vessel walls running education of prostacyclin, a small protein bodies, acting vasodilators.
diuretics act on the kidneys and see to it that are more sodium ions and chloride ions (salt) excreted along with their water solution. From the heart to be pumped liquid volume is reduced, so that the pressure drops in the blood stream. More important is that caused by the increased salt excretion decrease in sodium ion concentration in the smooth muscle of blood vessels (see above). They will thus become less sensitive to the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, the influence of the sympathetic nervous system decreases, and decreases in blood pressure.
Keywords: kidney The two bean-shaped kidneys consist of little more than 1 million units, the nephrons. Each nephron consists of a renal tubules and the associated. This is a blood renal glomeruli, in the arterial blood, venous blood flows in and out. It is surrounded by a tight-fitting, double-walled capsule, the gap in the coiled and looped tubules extending passes. This takes the tubules in the renal corpuscles from the blood filtered liquid, the primary urine. This filtrate contains the water, all other blood components, except for those who because of their size can not be filtered, so the blood cells (white and red blood cells, platelets) and blood proteins. In an adult flow in 24 hours around 1700 liters of blood through the kidneys, then about 170 liters of primary urine . Filtration In the tubules of the nephrons of the primary urine is concentrated, so that is excreted in 24 hours, only 1.5 liters of urine. By active transport (including energy costs) by using ion pumps, particularly sodium ions pass through the wall of the tubules from the inside out. Here, a concentration gradient set up so that water follows the sodium ion solution and together with these and other ions in the tubules flows at tight blood vessels. The liquid flow into the tubules and the liquid in the relevant blood vessels in opposite directions so that the counter current principle effectively is. Which here means the following: blood fluid which already has taken many sodium ions, separated flows, through the wall of tubules, as fluid in the tubules, which has lost little sodium ions (and flows in the opposite direction). Blood fluid with little sodium ions "encounters" of the fluid in the tubules, which is already relatively high in sodium ions "got rid" color.Download operations are under the influence of at least three signal substances (hormones). Aldosterone promotes the active sodium ion transport into the blood by stimulating the production of ion pumps that transport sodium and potassium ions in opposite directions. This increases of course something of the return flow of the solution water from the tubules into the blood, because relatively more sodium ions are transported as potassium ions. The potassium excretion takes but still noticeable. Adiuretin, a small protein bodies from the pituitary gland in the brain stem facilitates direct the return flow of water from the tubules into Blut.Das ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide), a protein that is released from the muscles of the atria, increased contrast, the sodium ion and thus the fluid excretion in the urine Harnkanälchen.Die increases also. are excreted in the urine many final metabolic waste products such as urea, uric acid, bile pigments, Medication, but all too abundantly absorbed salts. The kidneys have therefore regulate an important detoxification function and at the same time the mineral and water balance. Other objects of the kidney, the production of renin (see above) and of erythropoietin, one for blood formation in the bone marrow indispensable hormone.
The diuretics may be divided according to their sites of action in the various sections of the tubules:
thiazides act at the top of the ascending limb where they inhibit the active sodium ion and chloride ion transport. Potassium ions also excreted increased. Thiazides are known hydrochlorothiazide (Esidrix (R)) and Xipamide (Aquaphor (R)) .
loop diuretics act on the lower part of the ascending limb, shortly after the Henle loop and block where the active sodium ion, potassium ion and chloride ion transport, and calcium ions are excreted increased. The effect of loop diuretics is short but intense. It is to be feared relatively high potassium loss. furosemide (Lasix (R)) and torasemide (Unat (R)) are representative of this group of drugs.
potassium-sparing diuretics contribute in the last section of the tubules and are often antagonists (antagonists) of aldosterone. They suppress the aldosterone from its receptor inside the cell, so that the aldosterone no longer coupled to its receptor-enter the cell nucleus and can spark off the production of signaling proteins, the AIP's (aldosterone-induced proteins). The AIP's are nothing more than the already mentioned above, sodium-potassium ion pump to transport the two ions in opposite directions. Potassium-sparing diuretics increase the sodium ion excretion therefore, the potassium ions are held back against it. The diuretic effect is compared with the other Diuretics very weak. As an example, spironolactone is (Aldactone (R)) called . are often combined potassium-sparing diuretics with other diuretics. We then have a sufficient effect, yet no loss of potassium, as in spironolactone with hydrochlorothiazide (Spironothiazid (R)) or spironolactone with furosemide (Spiro comp (R)) . There are also potassium-sparing diuretics, aldosterone antagonists are not. They also act in the last section of the tubules. However, they block sodium channels there and thus inhibit the sodium ion-hydrogen ion exchange. In turn, the potassium ion excretion reduced. These potassium-wasting diuretics are usually combined with other diuretics, eg amiloride with hydrochlorothiazide (Diursan (R)) and triamterene with hydrochlorothiazide (Dytide H (R)) . should
nephron as the basic building blocks of the kidney (Wikipedia)
The procedure for drug high blood pressure treatment now are presented briefly in conclusion:
Mon otherapie
When monotherapy with one drug has to be changed several times, until one is found, to which the patient responds well and occur when no major side effects also. For the Mono Beta Blocker Therapy are , diuretics , calcium antagonists , ACE inhibitors and AT-II blockers .
occurs within 1-3 months, no beneficial effects one should be shifted to a double combination.
dual combination
The dual combination is superior to a monotherapy, as the effects of various agents potentiate and often reduces the side effects because the individual drugs can be dosed less. Therefore, it is in the modern treatment of high blood pressure over this, sooner rather than later drug combinations of two or even three drugs prescribed.
are typical dual combinations:
diuretic and beta blocker or calcium antagonist or ACE inhibitors or AT-II blockers
calcium antagonist and beta blocker or ACE inhibitors
not enough this, too, is switched to the triple combination.
triple combination
Here are typical:
diuretic and beta blockers and a directly vasodilator drug
diuretic and ACE inhibitors or AT-II blockers and calcium antagonist
diuretic and sympatholytic and a direct vasodilator drug
last resort
Should not everything to, you combine a potent diuretic with directly vasodilator minoxidil and alpha blockers . This combination is almost always effective, but is often poorly tolerated.
Jens Christian Heuer

